| When measuring large alternating current, it needs to be converted into a relatively uniform current for the convenience of secondary instrument measurement (China stipulates that the secondary rating of current transformers is 5A or 1A). In addition, the voltage on the line is relatively high if measured directly. is very dangerous. The current transformer plays the role of current conversion and electrical isolation. It is a sensor used by secondary equipment such as measuring instruments and relay protection in the power system to obtain electrical primary circuit current information. The current transformer converts high current into low current in proportion. The primary side of the current transformer is connected to the primary system, and the secondary side Connect to measuring instruments, relay protection, etc. During normal operation, the secondary side of the transformer is in an approximate short-circuit state and the output voltage is very low. During operation, if the secondary winding is open-circuited or an abnormal current flows through the primary winding (such as lightning current, resonant overcurrent, capacitor charging current, inductor starting current, etc.), an overvoltage of thousands or even tens of thousands of volts will be generated on the secondary side. . This not only causes harm to the insulation of the secondary system, but also causes the transformer to burn out due to overexcitation, and even endangers the life safety of the operating personnel. The primary side has only 1 to a few turns, and the wire cross-sectional area is large, and it is connected in series to the circuit under test. The secondary side has a large number of turns and a thin wire, forming a closed circuit with an instrument with a small impedance (current coil of an ammeter/power meter). The operation of the current transformer is equivalent to a transformer with a short circuit on the secondary side. The excitation current is ignored and the ampere turns are equal I1N1=I2N2. The current ratio of the primary winding current I1 and the secondary winding I2 of the current transformer is called the actual current ratio I1/I2=N2/N1=k. Excitation current is the main source of error. The accuracy level of the current transformer used for measurement is 0.2/0.5/1/3, 1 means that the transformation ratio error does not exceed ±1%, and there are also 0.2S and 0.5S levels. The accuracy level of the current transformer for protection is 5P/10P, and 10P indicates that the composite error does not exceed 10%. | The protective current transformer mainly cooperates with the relay device. When a fault such as short circuit overload occurs on the line, it provides a signal to the relay device to cut off the faulty circuit to protect the safety of the power supply system. The working conditions of the protective miniature current transformer are completely different from those of the measuring transformer. The protective transformer only starts to work effectively when the current is several times or dozens of times larger than the normal current. The main requirements for protective transformers are: 1. Reliable insulation, 2. Large enough and accurate limit coefficient, 3. Sufficient thermal stability and dynamic stability. The maximum primary current that a protective transformer can meet the accuracy level requirements under rated load is called the rated accuracy limit primary current. The accurate limit coefficient is the ratio of the rated accurate limit primary current to the rated primary current. When the primary current is large enough, the iron core will be saturated and unable to reflect the primary current. The accuracy limit coefficient represents this characteristic. The accuracy level of protective transformer is 5P and 10P, which means the allowable error is 5% and 10% at the rated accurate limit primary current. The inrush current when a line fails generates heat and electromagnetic forces, which the protective current transformer must withstand. When the secondary winding is short-circuited, the effective value of the primary current that the current transformer can withstand within one second without damage is called the rated short-time thermal current. When the secondary winding is short-circuited, the primary current peak that the current transformer can withstand without damage is called the rated dynamic stable current. Protection current transformers are divided into: 1. Overload protection current transformer, 2. Differential protection current transformer, 3. Ground protection current transformer (zero sequence current transformer) |
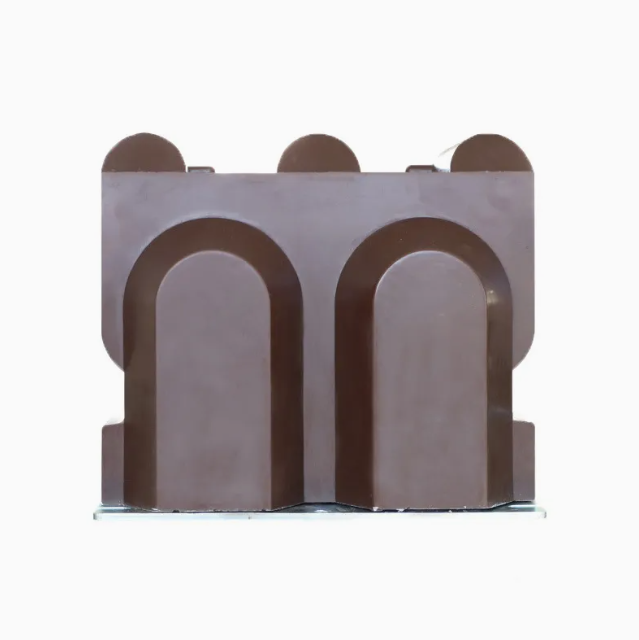
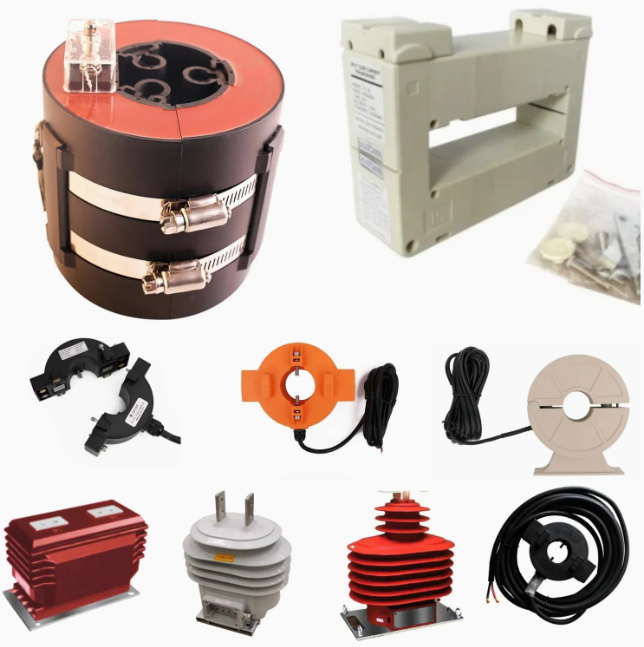
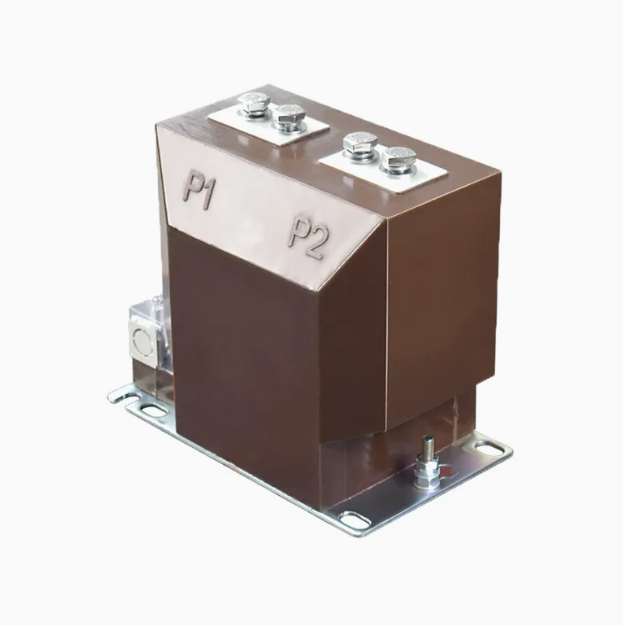
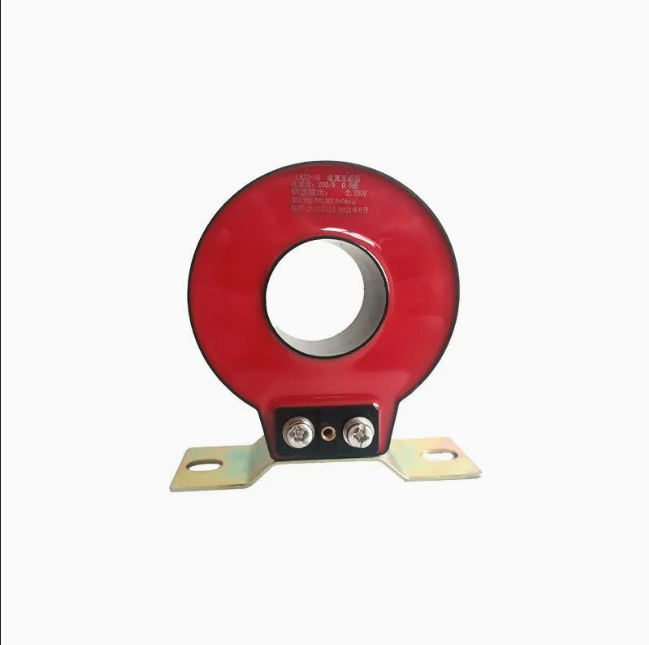
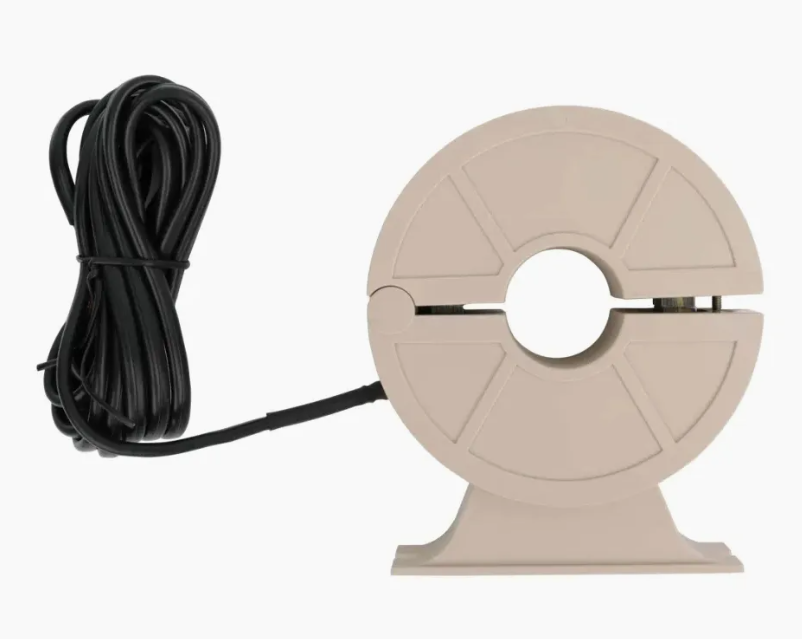
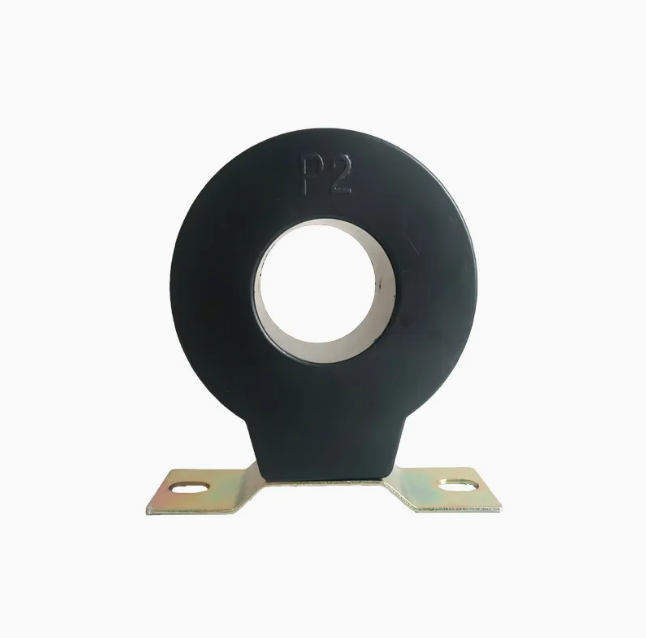


































 Note:
Note:

