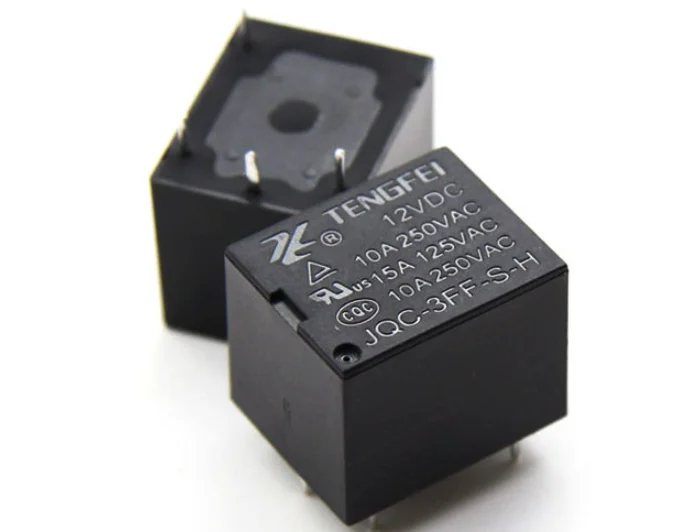
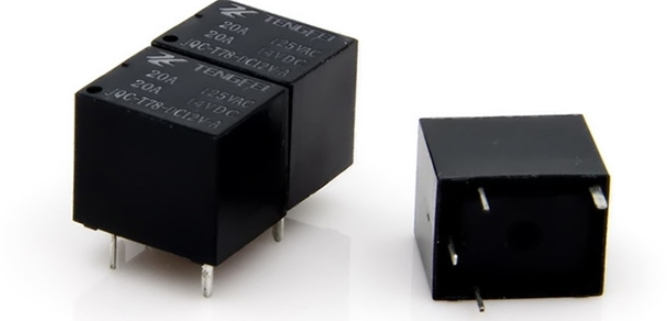
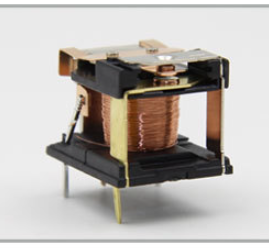
1$ per unit
basic information
| Contact Material | AgSn012 |
| Contact Form | 1Z(1C)\1H(1A) |
| Contact Ratings | N0:80A14VDC |
| Contact Resistance | 100mMax at6VDC 1A |
| Max Switching Current | 80A |
| Max Switching Voltage | 75VDC |
| Max Switching Power | 80A |
| Life Expectancy Electrical 100,000 Operations(at300perations/minute) | |
| Life Expectancy Machanical | 10,000,0000perations |



A relay is an electrically operated switch. It consists of a control circuit and a load circuit. When a small electric current passes through the control circuit, it can cause the relay to close or open the contacts in the load circuit. This allows a relatively small electrical signal to control a much larger current or voltage in another circuit. Relays are widely used in various electrical and electronic systems. For example, in industrial control systems, they can be used to start or stop motors. In automotive electronics, relays are often used to control high power components such as headlights and horns. They play an important role in ensuring the normal operation and safety of electrical equipment.
- 20Aswitching capability
- Smallsize auto relay
- Size15.7mm×12. 3mm×14mm(length*width*high)
COIL DATA ( at 20℃ )
| Nominal Voltage (VDC) | 5 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 24 | |
| Coil Resistance (Ω±10%) | 70 | 100 | 225 | 400 | 1600 | 0.36W |
| Rated Current (mA) | 71.4 | 60 | 40 | 30 | 15 | |
| Max Operate Voltage (VDC) | 3 . 75 | 4.5 | 6.75 | 9 | 18 | |
| Min Release Voltage (VDC) | 0 .40 | 0 .48 | 0 .72 | 0 . 96 | 1 . 92 | |
| Coil Resistance (Ω±10%) | 42 | 60 | 135 | 240 | 960 | 0.6W |
| Rated Current (mA) | 119 | 100 | 66 .7 | 50 | 25 | |
| Max Operate Voltage (VDC) | 3 . 25 | 3 . 9 | 5 . 85 | 7. 8 | 15 . 6 | |
| Min Release Voltage (VDC) | 0 .40 | 0 .48 | 0 .72 | 0 . 96 | 1 . 92 | |
| Coil Resistance (Ω±10%) | 31 | 45 | 100 | 180 | 720 | 0 . 8W |
| Rated Current (mA) | 161 . 3 | 133 . 3 | 88 . 9 | 66 .7 | 33 . 3 | |
| Max Operate Voltage (VDC) | 3 . 25 | 3 . 9 | 5 . 85 | 7. 8 | 15 . 6 | |
| Min Release Voltage (VDC) | 0 .40 | 0 .48 | 0 .72 | 0 . 96 | 1 . 92 | |
| Max Applicable Voltage | 130% of rated voltage at 70 ℃, 170% of rated voltage at 23 ℃ | |||||
CONTACT DATA
| Contact Form | 1H/1Z/1B |
| Contact Material | Silver Alloy |
| Load | Resistive load(COS Ф =1) |
| Contact Ratings | 20A 125VAC 20A 14VDC |
| Minimum load | 100mA 5VDC |
| Max Switching Voltage | 250VAC/14VDC |
| Max Switching Current | 25A |
| Max Switching Power | 2500VA/280W |
| Contact Resistance | 100mΩMax at 6VDC 1A |
| Life Expectancy | Electrical : 100,000 Operations(at30Operations/minute) |
| Mechanical : 10,000,000 Operations(at300Operations/minute) |
CHARACTERISTICS DATA
| Insulation Resistance | 100MΩMin at 500VDC |
| Dielectric Strength Between Open Contacts | 500VAC(for one minute) |
| Between Contacts and coil | 500VAC(for one minute) |
| Operate Time | 10ms |
| Release Time | 5ms |
| Temperature Range | -40℃ to+85℃ |
| Shock Resistance | Operating Extremes : 10G |
| Damage Limits : 100G | |
| Vibration Resistance | 10-55Hz, 1.5mm |
| Max. switching frequency | Mechanical:18,000operations/hr |
| Electrical:1,800operations/hr | |
| Humidity | 35-85% |
| Weight | Approx 6g |
Application Scenarios for Relays: Powering Diverse Industries
Relays are versatile and essential components in a wide range of industries, providing reliable switching and control solutions for various electrical and electronic systems. Below are some key application scenarios where relays play a critical role:
1. Industrial Automation
Relays are widely used in industrial control systems to manage machinery, conveyor belts, and production lines. They ensure precise switching of high-power equipment, enabling automation and improving operational efficiency.
2. Automotive Systems
In vehicles, relays are integral to controlling headlights, windshield wipers, fuel pumps, and starter motors. They provide reliable switching under harsh conditions, ensuring safety and performance in automotive electronics.
3. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning)
Relays are used in HVAC systems to control compressors, fans, and heating elements. They help regulate temperature and airflow, ensuring energy-efficient and comfortable environments.
4. Power Supplies and Inverters
Relays play a crucial role in power supply units and inverters by managing the switching between power sources, such as mains electricity and backup generators. They ensure uninterrupted power supply in critical applications.
5. Home Appliances
From washing machines and refrigerators to microwaves and air conditioners, relays are essential for controlling motors, heating elements, and other components in household appliances.
6. Telecommunications
In telecom infrastructure, relays are used to switch signals and control power distribution in communication equipment, ensuring reliable connectivity and network performance.
7. Renewable Energy Systems
Relays are employed in solar power systems and wind turbines to manage energy flow, battery charging, and grid connectivity, contributing to efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
8. Medical Equipment
In medical devices such as imaging systems, patient monitors, and laboratory equipment, relays ensure precise control and reliable operation, supporting critical healthcare applications.
9. Security Systems
Relays are used in alarm systems, access control, and surveillance equipment to enable secure switching and control, enhancing safety and protection.
10. Consumer Electronics
From smart home devices to entertainment systems, relays provide reliable switching and control, ensuring seamless operation of modern electronics.
Relays are the unsung heroes of modern technology, enabling efficient and reliable control across countless applications. Whether in industrial, automotive, or consumer settings, relays ensure that systems operate smoothly and safely. Choose high-quality relays to power your next project and experience the difference in performance and reliability!


![[Factory Direct Sales] GSM8 Series Motor Protection Circuit Breaker GSM8-3201](https://njzfelectric.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/qq2-2.jpg)